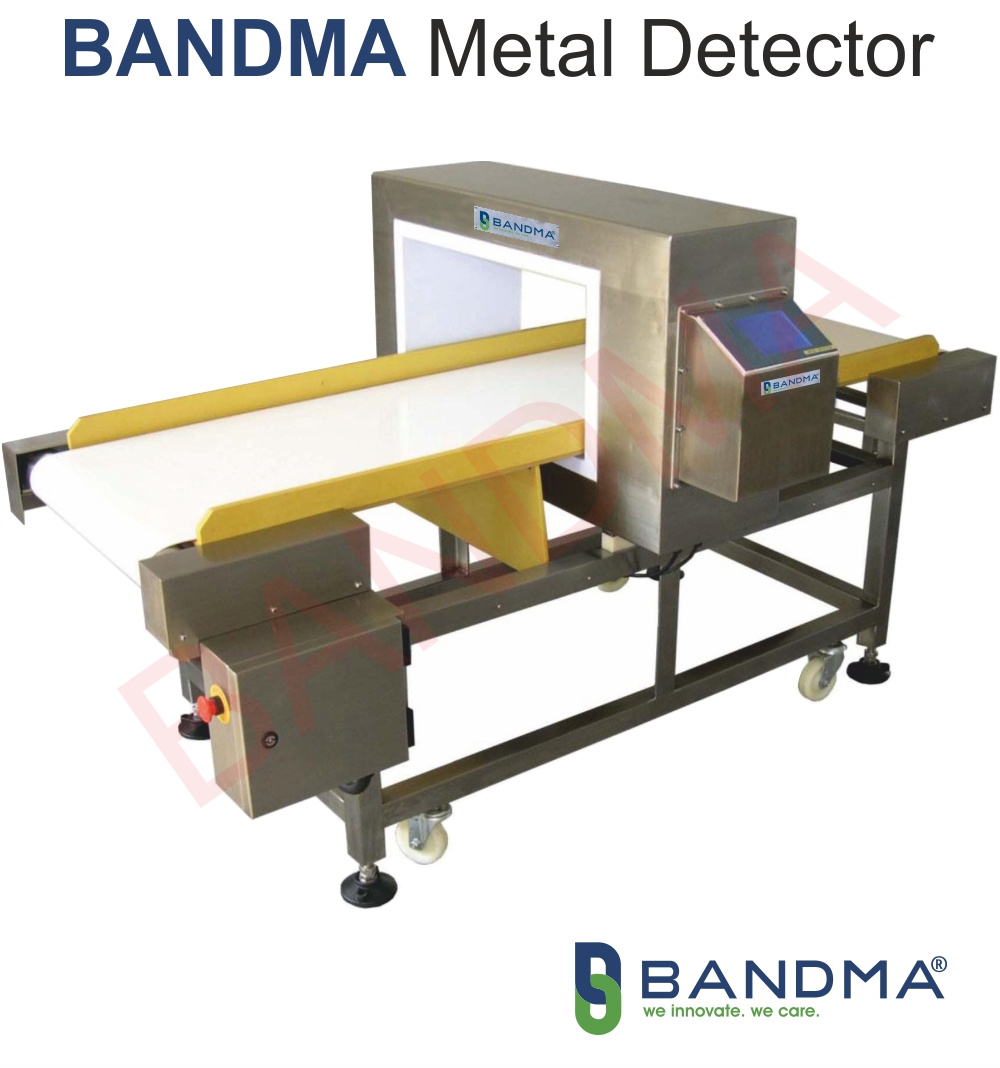
Metal detectors are most commonly connected to security checkpoints and beachside treasure hunts, their usefulness goes far beyond these well-known uses. Metal detectors are essential to maintaining product quality, safety, and operational effectiveness in the world of modern industry. This blog examines the many uses for metal detectors, examining their significance and the technology underlying these useful tools.
Bandma Gives Ensuring Product Quality in Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
The food and pharmaceutical industries, where product quality and safety are of utmost importance, are among the areas where metal detectors find crucial use. Food items may have metal contamination from a variety of sources, such as machinery, human error, and raw ingredients. Consumers may suffer serious injury from even the smallest metal shards, which can also result in expensive recalls.
At several stages of the production process, metal detectors are positioned strategically to detect and eliminate any metal contamination. These sophisticated detectors identify ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless steel particles, guaranteeing that the finished goods are free of dangerous impurities. Companies may safeguard their brand reputation and adhere to strict regulatory requirements by upholding high standards of product quality.
Safeguarding Manufacturing Equipment by Bandma
Metal detectors in production contexts protect costly gear while also protecting consumers. Production equipment may become contaminated by metal, necessitating expensive repairs and lost production time. Metal detectors, for example, are used in the textile sector to keep metal pieces from harming sewing machines and other machinery.
Businesses may prevent needless costs and preserve efficient manufacturing processes by identifying and eliminating metal impurities before they affect vital machinery. This proactive strategy prolongs the life of production equipment and improves overall operational efficiency.
Enhancing Security in Public Spaces
Metal detectors play an important part in security even though they are essential in industrial settings. Metal detectors are used at airports, government buildings, schools, and event sites to stop people bringing guns and other forbidden objects within. In order to protect the public, these gadgets offer a quick and non-intrusive way to screen people.
Discrimination capabilities, among other cutting-edge characteristics, enable modern metal detectors used in security applications to distinguish between potentially dangerous and innocuous metal objects. This accuracy makes security systems more effective and lowers false alarms, which makes the environment safer.
Revolutionizing Recycling Processes
Additionally, metal detectors are transforming the recycling sector. Metals and non-metallic components must be separated in recycling plants that handle large amounts of mixed materials. Metal detectors aid in the identification and classification of various metal types, improving recycling's effectiveness and environmental friendliness.
Metal detectors are used in e-waste recycling in addition to conventional recycling to collect valuable metals from abandoned electronic gadgets. Recycling plants can enhance sustainability efforts by optimizing material recovery and reducing waste through enhanced metal detection accuracy.
The Technology Behind Metal Detectors
Comprehending the technology underlying metal detectors illuminates their adaptability and efficiency. The mechanism of metal detectors is based on the electromagnetic induction principle. The receiver coil picks up a signal that is produced when a metal object enters the magnetic field of the detector. After that, the signal is examined to identify the kind and quantity of metal present.
Metal detectors come in a variety of forms, each ideal for a particular use case:
- Very Low Frequency (VLF) Detectors: VLF detectors are widely utilized in consumer applications and are perfect for finding jewels, coins, and antiquities. They have high discriminating and sensitive skills.
- Pulse Induction (PI) Detectors: Industrial and security settings use PI detectors because of their deep penetration. They are excellent at finding big metal objects and can work in difficult conditions like submerged or highly mineralized soils.
- Beat Frequency Oscillation (BFO) Detectors: BFO detectors are inexpensive, easy-to-use, and frequently found in consumer entry-level devices. For amateurs, they offer rudimentary metal detection capabilities.
Conclusion
It is impossible to exaggerate the significance of metal detectors in contemporary industry. Metal detectors are essential tools for protecting production equipment, boosting security, and guaranteeing the safety and quality of food and pharmaceutical items. Their use in recycling procedures emphasizes even more how important it is that they support sustainability.
Metal detectors are become more advanced as technology develops, providing improved sensitivity, discrimination, and adaptability. These gadgets are essential for all industries to uphold strict standards of efficiency, safety, and environmental responsibility. Whether in a public area, on a manufacturing floor, or at a recycling center, metal detectors are silently protecting our environment in ways that we frequently take for granted.